|
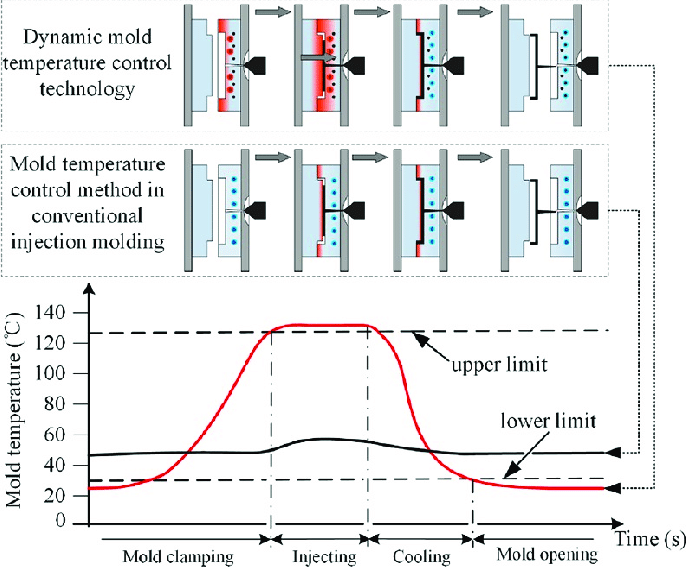
The Importance of Injection Mold Temperature Control
The Injection Mold Temperature refers to the surface temperature of the mold cavity in contact with the molded plastic part, which directly affects the flow of the melt, the coldness of the plastic part, and the quality of the plastic part. The labor productivity of the mold depends on the speed of the heat exchange of the mold, and the speed of the heat exchange of the mold depends on the temperature of the mold, the temperature of the melt, the demolding temperature of the plastic part, and the enthalpy of the plastic. For high-precision and long-life molds, the design of the injection mold temperature control system is very strict, and sometimes a special temperature regulator must be designed to strictly control the temperature of each part of the mold. The temperature control system of this type of injection mold is difficult. Different Plastics have different requirements for Injection Mold TemperatureReduced injection mold temperature will lessen stress cracking in plastics like PE, PP, HIPS, ABS, and other materials with good fluidity, Injection mold temperature should be kept at about 60°C. Increasing the injection mold temperature will help to reduce internal stress in plastic parts made of plastics with low fluidity, such as PC, hard PVC, PPO, and PSF. The Injection mold temperature should be kept between 80 and 120°C. Additionally, the cooling processes for non-crystalline plastics like PS, HIPS, PVC, PMMA, PC, ABS, and polysulfone and crystalline polymers like PE, PP, POM, PA, and PET are different. Heat is emitted yet the plastic’s temperature doesn’t change as cooling passes through the crystallization zone of crystalline polymers. The crystalline plastic must remove more heat during cooling than the amorphous plastic because the plastic cannot be further chilled until it has passed through the crystalline zone.
The following are the commonly used barrel temperature and Injection mold temperature when the surface quality of plastic parts has no special requirements (ie, general smooth surface). The mold temperature refers to the temperature of the surface of the core cavity.
Injection Mold Temperature directly impacts the plastic parts’ appearance and dimensional precisionThe plastic part is severely deformed after being removed from the mold due to the excessive mold temperature, uneven molding shrinkage, and ease of flashing and sticking. The surface of the plastic part will have weld lines or surface flaws like shrinkage dents or flow lines if the temperature is too low. It will also have poor melt fluidity and filling When the mold temperature is unequal, the temperature of the plastic component that has been molded is uneven after curing in the mold cavity. This uneven shrinkage causes internal tension, which leads to deformation, cracking, and warping of the plastic part after demolding. cooling of each component of the plastic part must be balanced to prevent distortion. The rate of shrinkage, dimensional stability, deformation, stress cracking, and surface quality of plastic components are all significantly impacted by changes in mold temperature.
The molding cycle is significantly impacted by mold temperatureAbout 80% of the entire molding cycle is made up of the cooling phase. Melt filling takes up around 5% of the remaining time, while ejection and mold opening and closing take up about 15%. As a result, the ideal option to shorten the production cycle for molds with high productivity needs is to lower the cooling time. |